Siblings of Parent: N lines containing two integers each representing the parent and child nodes of a tree are given as input to the program. Also, M integers are passed as input to the program. For each integer among M integers, the program must print the siblings of the parent as the output.
Note: The siblings must be printed in the order of their occurrence.
Boundary Condition(s):
1 <= N <= 1000
1 <= M <= 800
Input Format:
The first line contains N.
The next N lines contain two integers (parent and child) separated by space(s).
The (N+2)th line contains the value of M
The (N+3)th line contains M integers separated by space(s).
Output Format:
The first M lines contain the siblings of the parent of each node represented by M integers (one for each line).
Example Input/Output 1:
Input:
9
4 2
4 34
2 12
2 3
34 44
34 40
4 23
23 60
3 78
2
78 40
Output:
12
2 23
Explanation:
The tree formed is given below.
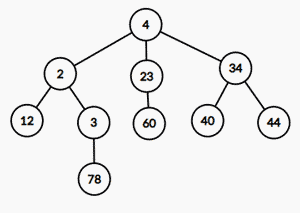
The parent of 78 is 3 and its sibling is 12.
The parent of 40 is 34 and its siblings are 2 and 23.
Example Input/Output 2:
Input:
11
5 6
2 3
5 2
3 56
5 8
5 7
6 89
89 54
89 63
89 52
52 69
3
69 89 3
Output:
54 63
2 8 7
6 8 7
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int k, n;
scanf("%d", & k);
int mat[k][2];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
scanf("%d%d", & mat[i][0], & mat[i][1]);
scanf("%d", & n);
int a[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", & a[i]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
if (a[i] == mat[j][1]) {
for (int l = 0; l < k; l++) {
if (mat[j][0] == mat[l][1]) {
for (int p = 0; p < k; p++) {
if (mat[p][0] == mat[l][0] && p != l)
printf("%d ", mat[p][1]);
}
printf("n");
break;
}
}
break;
}
}
}
}

Leave a Reply